What it costs to. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.

Ap Econ 6 34 Inflation And Unemployment The Phillips Curve Flashcards Quizlet
The fall of the unemployment rate.

Unemployment rate definition economics quizlet. Key Points The natural rate of unemployment is the unemployment rate when the economy is producing at its full potential output. The unemployment rate is calculated by dividing the number of unemployed people by the potential labor force and then times 100 to get the percentage of people unemployed. The unemployment rate should remain near zero.
Crop and resource shortages. Start studying Economics Unemployment. Unemployment due to people being in the process of moving from one job to another.
Not in the labor force. Is a retired person considered unemployed. The unemployment rate measures the share of workers in the labor force who do not currently have a job but are actively looking for work.
Unemployment occurs when a person who is actively searching for employment is unable to find work. What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics. It is a lagging indicator meaning that it generally rises or falls in the wake of changing economic conditions rather than.
Which branch of economics describes the unemployment rate in a given year. The rate of unemployment will be very high during economic booms. Lost output income consumption resources are not.
We would expect to have some unemployment due to normal structural and frictional factors. Unemployment resulting from industry reorganization usually through technological advancements. Technology can help governments handle economic emergencies such as.
Unemployment is often used as a measure of the health of the economy. The unemployment rate measures the share of workers in the labor force who do not currently have a job but are actively looking for work. Employers can hire workers from all over the world.
Who is the richest architect in the world. According to a 2009 report by economists John Schmitt and Dean Baker of the Center for Economic and Policy Research it is difficult to accurately compare for example the unemployment rate. Unemployment rate number of unemployed expressed as a percentage of the labour force labor force participation rate The labour force participation rate LFPR or economic activity rate EAR is the ratio between the labour force and the overall size of their cohort national population of the same age range.
People who have not looked for work in the past four weeks are not included in this measure. Unemployed Labor Force x 100. The reliance on automation.
The economics of groups of decision making units government sector business sector household sector financial intermediaries. People who have not looked for work in the past four weeks are not included in this measure. All of the goods that are used in the production process.
Unemployment resulting from downturns in economic growth. When there is a decrease in the unemployment rate quizlet. The unemployment rate is the percent of the labor force that is jobless.
Instant sales and communication. Calculating the Unemployment Rate Remember that the unemployed are those who are out of work and who are actively looking for a job. What are the costs of unemployment quizlet.
The unemployment rate is calculated as. The economics of individual decision-making units households firms v. Choose from 500 different sets of unemployment chapter 12 economics flashcards on Quizlet.
Land labor capital and other primary inputs into production Question 3 1 point Marginal cost is Question 3 options. Microeconomics Macroeconomics Question 2 1 point Factors of production refer to Question 2 options. Frictional unemployment is caused by an inability for workers and employers to find each other immediately.
The employmentpopulation ratio should average 100 percent. Unemployment rate The unemployment rate represents the number of unemployed people as a percentage of the labor force the labor force is the sum of the employed and unemployed. This natural rate is positve rather than zero due to frictional and structural unemployment.
We can calculate the unemployment rate by dividing the number of unemployed people by the total number in the labor force then multiplying by 100. Learn unemployment chapter 12 economics with free interactive flashcards.
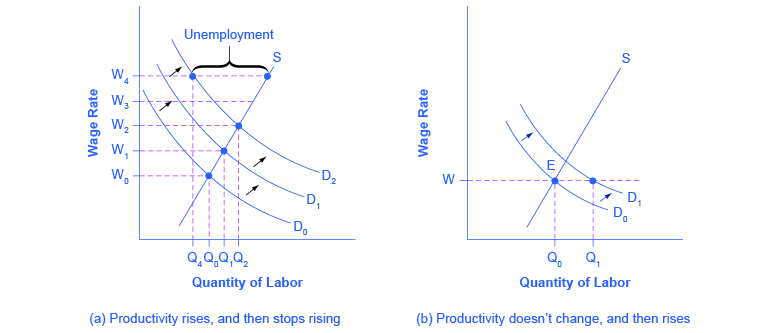
21 4 What Causes Changes In Unemployment Over The Long Run Principles Of Economics

Econ Ch 8 1 Flashcards Quizlet

Econ Test Unemployment And Inflation Flashcards Quizlet
Unemployment Definition Types Of Unemployment

Economics Chapter 13 Section 1 And 2 Flashcards Quizlet

8 Ways Incentive In Macro Economics Can Improve Your Business Incentive In Macro Economics Https Macro Economic Com 8 Economics Incentive What Is Economics

Econ Ch 8 1 Flashcards Quizlet

Macro Econ Chapter 28 Unemployment Flashcards Quizlet

Macroeconomics Flashcards Quizlet

Ap Econ 6 34 Inflation And Unemployment The Phillips Curve Flashcards Quizlet

Unemployment Flashcards Quizlet
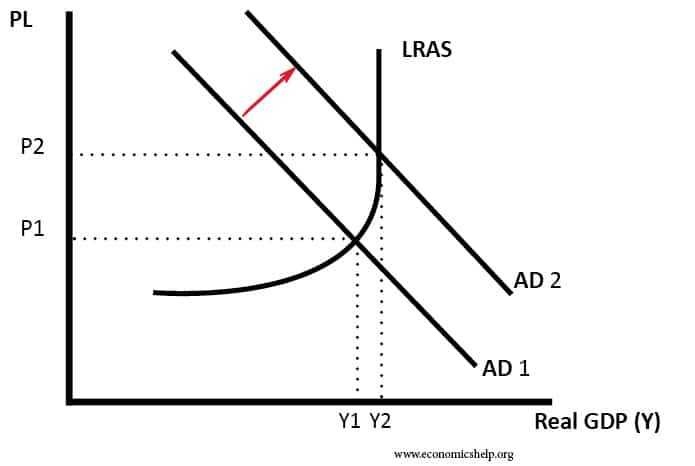
Definition Of Full Employment Economics Help

Unemployment Flashcards Quizlet

Macroeconomics Chapter 6 Notes Flashcards Quizlet
Understanding Supply Side Economics

Economics 2 6 3 Supply Side Policies A Level Flashcards Quizlet

Five Precautions You Must Take Before Attending The Economist The World In 10 The Economist The World In 10 Https Macro Economic C You Must Economist World

Labor Economics Employment Unemployment Lfp Flashcards Quizlet
Unemployment Rate Definition Economics Quizlet. There are any Unemployment Rate Definition Economics Quizlet in here.
Search This Blog
Blog Archive
- August 2023 (2)
- November 2022 (14)
- April 2022 (1)
- February 2022 (6)
- January 2022 (1)
- August 2021 (10)
- May 2021 (6)
- January 2021 (20)
Labels
- angelus
- apple
- april
- birthday
- blank
- Brisbane
- cards
- checklist
- chicken
- coloring
- Conditioner
- cupcake
- drumstick
- fighter
- fortnite
- fried
- greeting
- india
- jewish
- Keeprite
- lacing
- letters
- livescoreimsoccerfutbol24
- Malaysia
- Near
- office
- page
- pager
- pages
- Panasonic
- Parts
- planner
- Portable
- printable
- printables
- Profile
- quizlet
- Repair
- Service
- Services
- Shelf
- sketch
- Southside
- spare
- Stage
- template
- templates
- unemployment
- wallpaper
- world
- yesterday
